Buying guide for pressure transmitters
The pressure transmitters are indispensable in various industrial and technological applications.

From the origin andunit of pressure measurement to the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of sensor, you'll discover what a pressure transmitter is, how it works, and how a pressure transmitter operates.
We'll also look at the composition of a pressure transmitter, the types of output signals, and the essential criteria for choosing an industrial pressure transmitter . Exploring the different categories of pressure transmitters - differential, absolute pressure transmitter differential, pressure transmitter absolute or gauge pressure - we'll guide you on how to calibrate, install and test them effectively.
Finally, we'll look at pressure transmitter configuration and the practical applications of this essential field instrument, weighing up its advantages and disadvantages.
- Pressure measurement unit
- What is pressure transmitter ?
- What is the principle of a pressure sensor?
- How does a pressure transmitter work?
- Building a pressure transmitter ?
- What is the output signal of a pressure transmitter ?
- How to choose an industrial pressure transmitter ?
- Differential, absolute or gauge pressure: the different types of pressure transmitters ?
- How to calibrate a pressure transmitter?
- How to install an industrial pressure transmitter
- How to test pressure transmitter ?
- How do I configure pressure transmitter ?
- What are the applications of pressure transmitters ?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of pressure transmitters ?
Pressure measurement origin
 The Pascal unit of measurement is named after the renowned French philosopher, physicist and mathematician. Blaise Pascal.
The Pascal unit of measurement is named after the renowned French philosopher, physicist and mathematician. Blaise Pascal.
Born in Clermont-Ferrand, where the production unit of Fuji Electric France SAS, a French manufacturer of pressure transmitters industrial products, is headquartered, Pascal carried out a fundamental experiment by transporting a barometer to the summit of the Puy de Dôme, to prove thatatmospheric pressure decreases with altitude above sea level .
However, Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli was the pioneer in demonstrating the pressure exerted by the weight of the volume of air on the earth, and designed the first mercury-based barometer.
Pressure measurement unit
 The firstssion p is expressed in units of force F per unit area A : p = F / A
The firstssion p is expressed in units of force F per unit area A : p = F / A
Know the pressure units and their conversion is important for making the right choice of scales for your pressure transmitter industrial.
- Pascal (Pa): the International System (SI) base unit for pressure. One Pascal corresponds to 1 Newton per square meter (1 Pa = 1 N/m²).
- Bar (Bar): a unit of pressure commonly used in industrial applications. One Bar corresponds to a pressure of 100,000 Pa.
- Standard atmosphere (atm): used to express barometric or atmospheric pressure. One atmosphere corresponds to a pressure of 101,325 Pa.
What is pressure transmitter ?
 The pressure transmitter is also called pressure transmitter, pressure sensor, pressure gauge or pressure transducer. There is no significant difference between these different names. However, a distinction can be made between pressure transducers and smart pressure transmitters.
The pressure transmitter is also called pressure transmitter, pressure sensor, pressure gauge or pressure transducer. There is no significant difference between these different names. However, a distinction can be made between pressure transducers and smart pressure transmitters.
If we refer to the definition of a pressure transmitter, it is a pressure sensing device whose principle consists in converting the force applied by the pressure of a fluid on a given surface (deformation) into an electrical signal.
Industrial companies use pressure transmitters to :
- Measure pressure with a gauge pressure or absolute sensor.
- Flow measurement with a depressurizer and a differentialpressure transmitter
- Level measurement at pressure transmitter hydrostatic
- Measuring density with a differential pressure transmitter
What is the principle of a pressure sensor?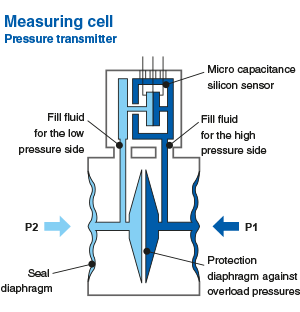
The fluid pressure is applied to an internal measuring component via a fitting and then a mechanical interface - measuring diaphragm made of stainless steel, ceramic or another noble material.
The electronic measuring element converts the pressure into a raw output signal.
How does a pressure transmitter work?
There are different technologies, methods, techniques and measurement principles for pressure transmitters models, each adapted to specific applications in the fields of process automation and industrial plants.
 The piezoresistive pressure sensor measures the force applied to a metal membrane. The stress exerted on a thin film causes it to deform, transmitting the pressure variation via an incompressible fluid (oil or water). This deforms a piezoresistive silicon element (Wheatstone bridge circuit). This component, using semiconductors, is a variable electrical resistor that converts the deformation into an ohmic value. The MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are also used in some of these sensors, offering miniaturization and greater sensitivity.
The piezoresistive pressure sensor measures the force applied to a metal membrane. The stress exerted on a thin film causes it to deform, transmitting the pressure variation via an incompressible fluid (oil or water). This deforms a piezoresistive silicon element (Wheatstone bridge circuit). This component, using semiconductors, is a variable electrical resistor that converts the deformation into an ohmic value. The MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are also used in some of these sensors, offering miniaturization and greater sensitivity.- The pressure transmitter capacitive sensor measures the force applied to a stainless steel or ceramic metal diaphragm. The pressure exerted deforms the metal film, which transmits the pressure variation via an intermediate incompressible fluid (oil or water). This deforms a capacitive silicon element. This component is a variable capacitor which converts the deformation into a capacitive value.
- The frequency resonance transmitter uses specific terms such as BFSL (Best Fit Straight Line) to define the linearity of the measurement. This pressure transmitter converts pressure variation into a change in oscillation frequency, offering high resolution and a variety of solutions for different applications.
- The pressure transmitter strain gauge or strain gage sensor works in a similar way, where the sensor's output signal is then filtered, amplified, temperature-compensated and formatted into an analog signal. The analog output is transmitted via an electrical connector, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
- Pressure gauges,on the other hand, feature a local display of the pressure measurement.U-tube manometers, for example, are often used for simple, direct measurements.
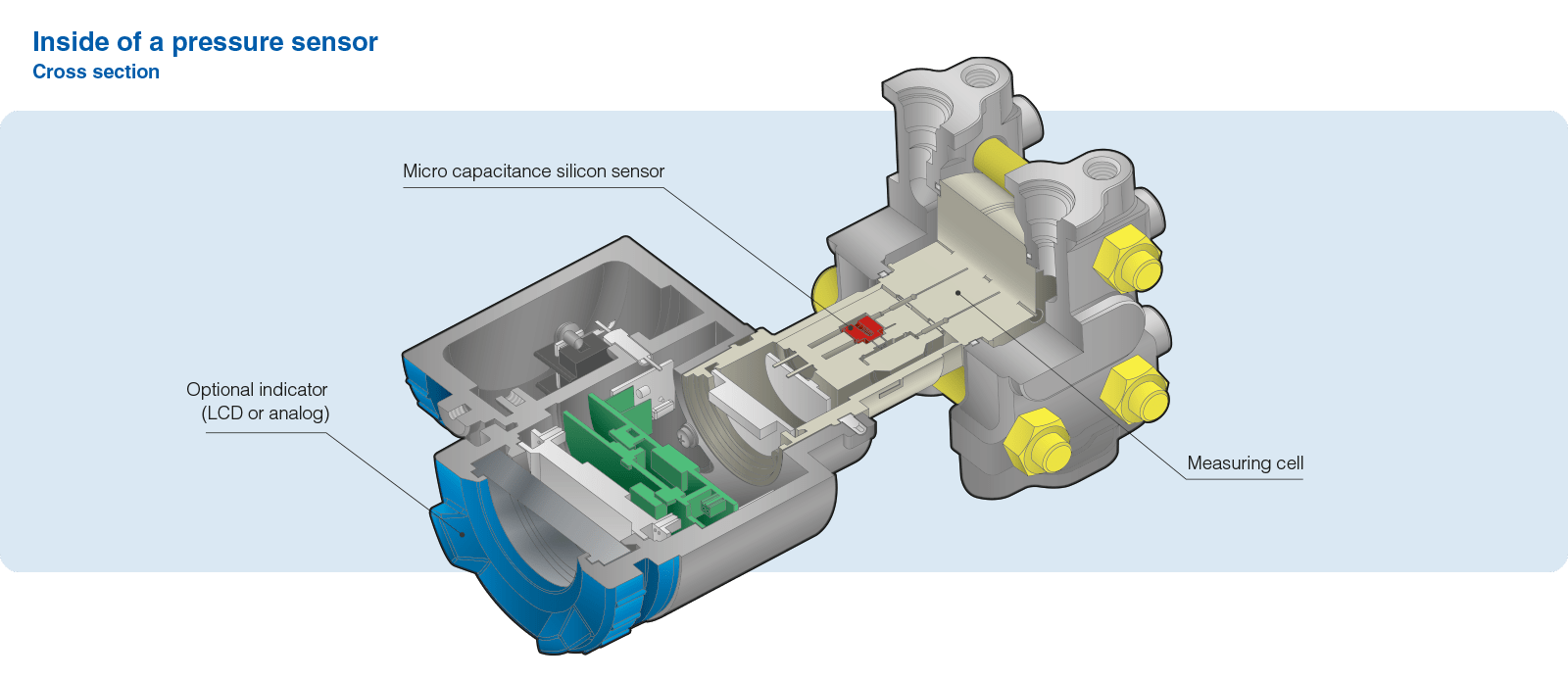
Construction of the pressure transmitter
The construction of a pressure transmitter comprises several essential elements:
- a mechanical connector for mounting,
- a metallic or ceramic membrane,
- a capacitive sensor or piezoresistive detector,
- a filling fluid, often oil, integrated into the pressure cells to transmit pressure variations,
- electronic module for conditioning and amplifying the detector signal,
- an electrical connector for easy connection to other automation systems,
- a plastic or metal housing (aluminum, stainless steel, stainless steel),
- a digital indicator (optional) to display pressure information in real time.
 What is the output signal of an industrial pressure transmitter ?
What is the output signal of an industrial pressure transmitter ?
The signal from a pressure sensor can be either analog or digital. The analog signal from pressure transmitter is usually a 4-20mA current output, a 0-10V voltage output or a 1-5V voltage output. The output signal is sent to the control unit in order to act on the control unit.
The 4-20mA analog output signal is commonly used by these devices because of the many advantages it offers.
 First of all, the pressure transmitter 4-20 mA is resistant to signal loss due to the transmission line, guaranteeing accurate measurement.
First of all, the pressure transmitter 4-20 mA is resistant to signal loss due to the transmission line, guaranteeing accurate measurement.
It also extends the distance between pressure transmitter and the system concerned. In addition, the absence of current makes it possible to detect line faults, facilitating troubleshooting. The 4-20mA 2-wire or 4-wire pressure transmitter is also less sensitive to electromagnetic interference, which guarantees its reliability.
Finally, it can be used in a 4-20mA loop to power several devices such as the display, controller and recorder.
Digital communication is available with various communication protocols - HART - Fieldbus - Profibus - Modbus. These communication protocols not only transmit the measured value, but also enable pressure measurement devices to be configured. These are known as SMART electronic transmitters. Some pressure transmitters electronic transmitters also offer IO Link interfaces, a range of specific measurement accuracies and ranges, and international approvals.
How to choose an industrial pressure transmitter ?
The industrial pressure transmitter must be selected according to the fluid to be measured, the pressure range and the operating conditions of the application and process.
 Properties of the fluid to be measured such that : pressure transmitter air, pressure transmitter gas, pressure transmitter hydrogen, pressure transmitter steam, pressure transmitter water or other liquid, as well as its characteristics (density, viscosity, corrosivity, etc.).
Properties of the fluid to be measured such that : pressure transmitter air, pressure transmitter gas, pressure transmitter hydrogen, pressure transmitter steam, pressure transmitter water or other liquid, as well as its characteristics (density, viscosity, corrosivity, etc.).- Process operating conditions: pressure to be measured, static pressure, process temperature, risk of corrosion
- The type of measurement: pressure measurement, Differential Pressure (DP) flow measurement, hydrostatic level measurement, density measurement
- The type of pressure to be measured :
- Gauge pressure
- Atmospheric pressure
- Absolute pressure
- Differential pressure
- Barometric pressure
- The pressure range or measuring span
- The turndown ratio or rangeability
- The accuracy of pressure measurement
- The response time
- Mechanical mounting interface or process connection fitting: screw connection, flange connection
- Analog output signal and/or wired or wireless digital communication
- The climatic environment and associated constraints:

- Industrial environment, associated constraints, current regulations:
 Functional safety and safety integrity level (SIL) ; IEC 61508 standard and IEC 61511 standard that require pressure transmitters with advanced SIL2/SIL3 safety functions.
Functional safety and safety integrity level (SIL) ; IEC 61508 standard and IEC 61511 standard that require pressure transmitters with advanced SIL2/SIL3 safety functions.
The choosing a pressure sensor with the right level of safety and choosing the safest sensor for hazardous areas are essential for the safety and longevity of your process.- Burst pressure must be taken into account when dimensioning pressure transmitters. The burst pressure corresponds to the mechanical stress limit of the enclosure, and when it exceeds this threshold, the enclosure is destroyed, which can lead to fluid leakage. Keeping the pressure within the specified range guarantees reliable measurements in accordance with the data sheet.
- Accessories for pressure transmitter such as a manifold or cable gland.
Differential, absolute or gauge pressure: the different types of pressure transmitters ?
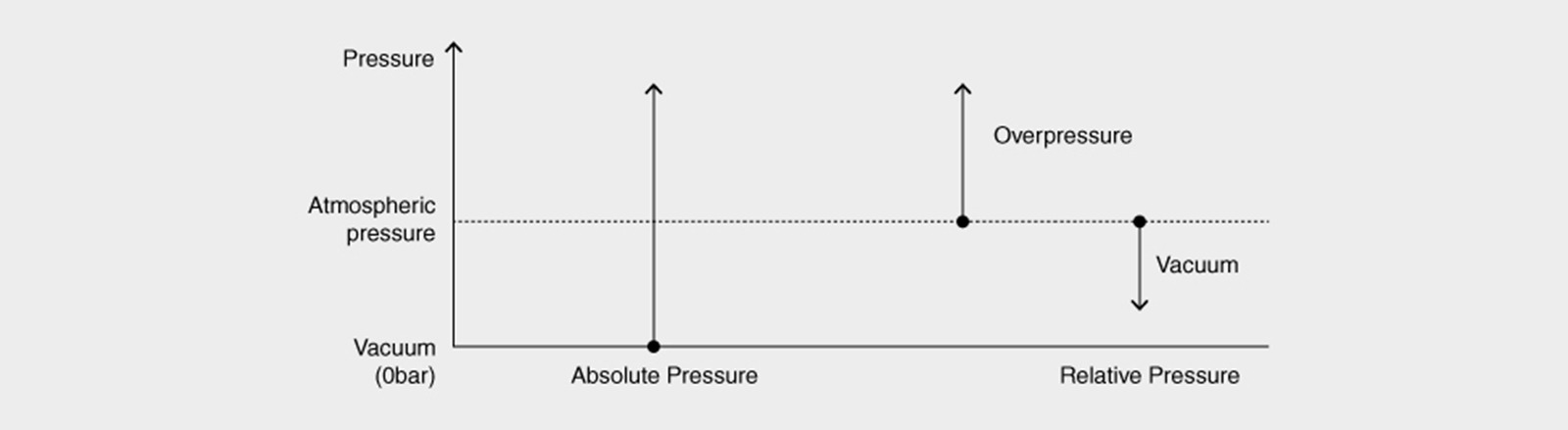
The gauge pressure transmitter enables measurement of gauge pressure of the process in relation to atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure is measured using a reference cavity inside the transmitter. This pressure decreases as altitude increases.
The pressure transmitter differential uses two separate chambers connected by a flexible diaphragm. Pressure is measured on either side of the diaphragm. The differential pressure (dp) is the pressure difference between these two pressures: a reference pressure on the low pressure side (BP or LP) and a pressure on the high pressure side (HP). This differential pressure meter is used to measure fluid flow in pipelines, monitor filter clogging or calculate pressure drops.
The pressure transmitter absolute compares gauge pressure with absolute vacuum. Absolute pressure is always positive. The advantage of this device is that it can operate independently of variations in atmospheric pressure, thanks to a vacuum reference chamber, for greater accuracy.
Absolute pressure is expressed from gauge pressure by adding 1.013 bar, i.e. p. absolute (bar abs.) = p. gauge (bar) + 1.013.
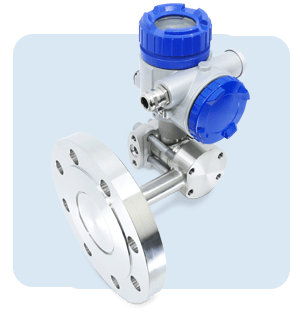
A pressure transmitter with diaphragm seal diaphragm separates the process medium being measured from the pressure cell. The diaphragm and contact parts are made of a material resistant to the fluid being measured, and are welded to the base of the pressure cell.
A capillary tube or connecting sleeve provides the link between the separating diaphragm and the pressure cell. This space must be degassed under vacuum, then filled with oil and sealed. The measured pressure exerts a force on the outer surface of the diaphragm. As the diaphragm flexes inwards, it attempts to compress the filling fluid inside the instrument.
This filling liquid is designed to resist compression, so the force is channeled directly to the pressure-measuring cell. The entire operation of a pressure transmitter diaphragm is based on Blaise Pascal's principle.
The pressure transmitter diaphragm is manufactured from a variety of materials including stainless steel, titanium, Inconel, Hastelloy, Monel, Tantalum, ceramic and Nickel. The materials used depend on the type of application and temperature for which the industrial pressure transmitter is designed.
The pressure transmitter with diaphragm seals is used to measure fluid pressures in the high-temperature range.

- The pressure transmitter multivariable
The multivariable pressure transmitter combines differential pressure measurement, absolute pressure measurement and temperature measurement in a single sensor. These products are used in particular for mass flow measurement.
The hydrostatic level sensor is a measuring device used to determine the filling level of a liquid in tanks or vessels. The measuring principle is based on hydrostatic pressure, which is the weight exerted by a liquid as a function of the height of the filling column.
- The immersed pressure sensor
This submersible or hydrostatic pressure sensor can be immersed in a liquid to measure the level in a tank or reservoir. The submergedpressure transmitter is generally fitted with a stainless steel diaphragm.
How to calibrate a pressure transmitter?
 Visit industrial pressure transmitters require periodic calibration to ensure industrial metrology throughout their life cycle and avoid factors that influence the accuracy of your sensors.
Visit industrial pressure transmitters require periodic calibration to ensure industrial metrology throughout their life cycle and avoid factors that influence the accuracy of your sensors.
The calibration period is defined by the manufacturers of pressure transmitters. Zero and span calibration is required.
At the factory or at the laboratory, the accuracy is verified at several points in the pressure range to check the linearity of the output signal over the entiere range.
Calibration involves applying a defined reference pressure to the sensor's mechanical interface, checking the 4-20 mA output signal and then applying compensation. The sensor can be calibrated using an external adjusting screw, a programming interface or programming software. For pressure transmitter models with display and pushbuttons, local calibration is possible.
In order to carry out the various manipulations, it may be necessary to have an isolating valve or manifold mounted on the pressure transmitter to isolate it from the process.
For your annual calibrations, you can call on a company specializing in pressure transmitters calibration.
Regularcalibration of pressure transmitter ensures accurate pressure measurement for consistent results.
How to install a pressure measurement system for industry ?

Pressure transmitters can be attached to the Primary Elements for DP Flow or to the pipe where the pressure is to be measured, by means of a mechanical process connection.
Special installation precautions must be taken depending on the process pressure and temperature conditions.

The 4-20 mA output signal of this device can be connected to a display system (an industrial digital display, a recorder, a controller, or a supervision system) or to a PLC (automation system for pressure measurement) in order to control a control device and regulate the pressure of a process.
For your own safety, check the wiring diagram on pressure transmitter before wiring the field instrument.
If you need help, we recommend that you call in a professional company to install and commission your measuring instrument.
How to test pressure transmitter ?
 A pressure transmitter 4-20 mA can be tested by applying a defined known pressure to the mechanical interface of the pressure sensor and checking the measured analog output signal. If you have a pressure transmitter with displaycheck the value displayed on the indicator.
A pressure transmitter 4-20 mA can be tested by applying a defined known pressure to the mechanical interface of the pressure sensor and checking the measured analog output signal. If you have a pressure transmitter with displaycheck the value displayed on the indicator.
If your instrument is faulty, you can ask a specialist or one of the manufacturers of industrial sensors to repair it for you.
If repair is not possible, you can replace your old pressure transmitter reference with a new, more modern model.
How do I configure pressure transmitter ?

Intelligent digital transmitters with HART protocol can be configured :

What are the applications of pressure transmitters ?
 Understanding why measure pressure in the process industries is important to guarantee safety, optimize process control, improve energy efficiency and maintain the quality of finished products.
Understanding why measure pressure in the process industries is important to guarantee safety, optimize process control, improve energy efficiency and maintain the quality of finished products.
The pressure transmitter is used in many industrial applications.
This digitalpressure transmitter can detect pressures ranging from a few millibars to several hundred bars. It is therefore essential in a wide range of industries for the automation of production lines and machines.
Gauge or absolute compressed air pressures, water pressures, steam pressures and gas pressures can all be measured.
Applications include differential pressure measurement of liquid flow, gas flow or vapor flow in a pipe, filter monitoring, liquid level measurement in a tank with a pressure transmitter flush diaphragm, fluid density measurement.
Depending on your industry, you need to choose the right measuring instrument for your application and the constraints of your industrial environment.
What are the advantages and disadvantages
of a pressure transmitter ?
Advantages of pressure transmitters
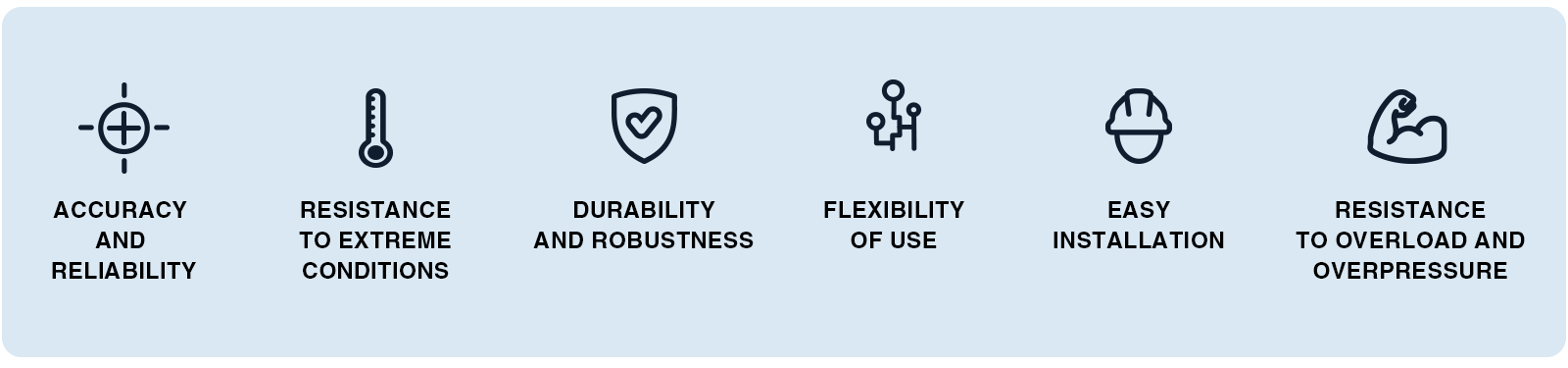
- Accuracy and reliability: pressure transmitters offer extremely precise measurements, essential for industrial applications. They increase productivity and reduce costs by providing precise information on the pressure of gases, vapors or liquids.
- Resistance to extreme conditions: Even in high-temperature or corrosive environments, such as those encountered in the chemical or oil & gas industries, operation is guaranteed with exceptional reliability and precision.
- Durability and robustness: housed in stainless steel or aluminum enclosures, pressure transmitters resist shock, vibration and hostile environments. They're built to last.
- Flexibility of use: Available in a variety of designs and technologies, these sensors cover a wide range of pressure measurement ranges for all fluids, including vacuum and negative-pressure applications. Their flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries.
- Easy installation: With a wide variety of fittings and connectors available, pressure transmitters can be integrated quickly and easily into automation systems, minimizing installation errors.
- Resistance to overload and overpressure: Thanks to their high resistance to overload, pressure transmitters can withstand extreme pressure peaks, such as those produced by rapidly closing valves or compressed air pressure surges.
Disadvantages of pressure transmitters
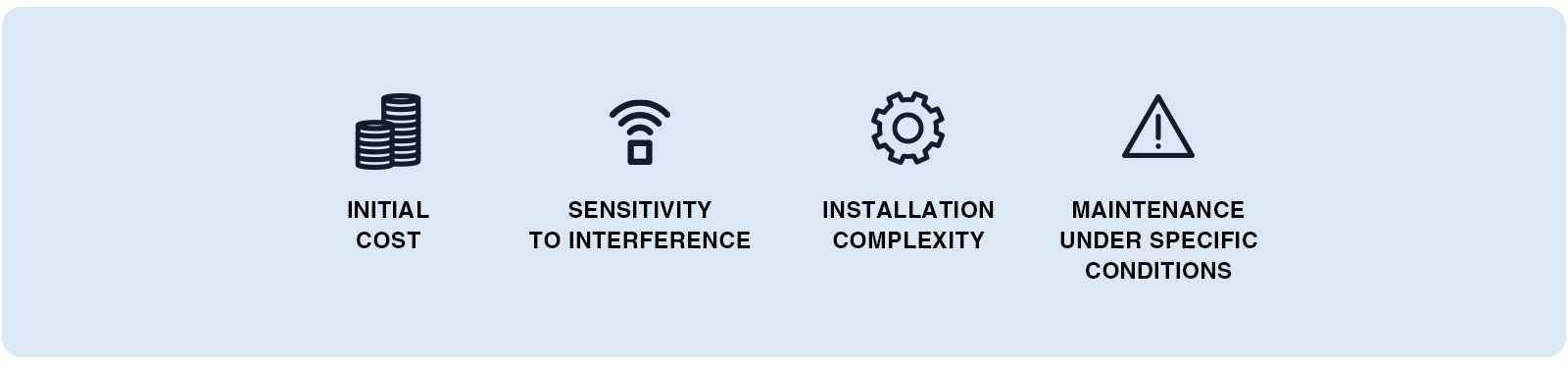
- Initial cost: The cost of acquiring high-precisionpressure transmitters can be high, representing a significant investment for some industrial companies. The price of a pressure transmitter often reflects its quality and durability. Avoid exotic pressure transmitters brands and turn to a French pressure transmitter manufacturer.
- Sensitivity to interference: Sensors using semiconductors can be sensitive to electromagnetic interference, which can affect their accuracy. Opt for a manufacturer offering EMC-compliantpressure transmitter .
- Installation complexity: While many sensors are designed for easy installation, some complex applications may require specific technical skills to ensure optimal operation. Rely on a trusted pressure transmitter manufacturer.
- Maintenance under specific conditions: In certain installations, particularly where environmental conditions are extreme, regular maintenance of your pressure transmitter may be necessary to guarantee performance. Choose a manufacturer of pressure transmitter with a local maintenance service.
Measuring pressure can't be improvised!
 Visit pressure measurement requires call in the professionals in the instrumentation sector.
Visit pressure measurement requires call in the professionals in the instrumentation sector.
The experts at Fuji Electric, the French manufacturer of pressure transmitters industrial pressure gauges, will guide you and offer you pressure transmitters , designed for your most demanding application, to ensure that you get the performance and results you expect, and to avoid errors in your process pressure measurement. So you can enjoy the benefits of pressure transmitter without the drawbacks.
Fuji Electric'spressure transmitters are renowned for their high technology, pressure measurement accuracy, wide measurement range, long-term stability, build quality, reliability, durability, technical support, easy return policy and fast delivery service for customers.



































 The Pascal unit of measurement is named after the renowned French philosopher, physicist and mathematician.
The Pascal unit of measurement is named after the renowned French philosopher, physicist and mathematician. 
 The pressure transmitter is also called pressure transmitter, pressure sensor, pressure gauge or pressure transducer. There is no significant difference between these different names. However, a distinction can be made between
The pressure transmitter is also called pressure transmitter, pressure sensor, pressure gauge or pressure transducer. There is no significant difference between these different names. However, a distinction can be made between 
 The piezoresistive pressure sensor measures the force applied to a metal membrane. The stress exerted on a thin film causes it to deform, transmitting the pressure variation via an incompressible fluid (oil or water). This deforms a piezoresistive silicon element (Wheatstone bridge circuit). This component, using semiconductors, is a variable electrical resistor that converts the deformation into an ohmic value. The MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are also used in some of these sensors, offering miniaturization and greater sensitivity.
The piezoresistive pressure sensor measures the force applied to a metal membrane. The stress exerted on a thin film causes it to deform, transmitting the pressure variation via an incompressible fluid (oil or water). This deforms a piezoresistive silicon element (Wheatstone bridge circuit). This component, using semiconductors, is a variable electrical resistor that converts the deformation into an ohmic value. The MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are also used in some of these sensors, offering miniaturization and greater sensitivity.
 What is the output signal of an industrial pressure transmitter ?
What is the output signal of an industrial pressure transmitter ? First of all, the pressure transmitter 4-20 mA is resistant to signal loss due to the transmission line, guaranteeing accurate measurement.
First of all, the pressure transmitter 4-20 mA is resistant to signal loss due to the transmission line, guaranteeing accurate measurement.
 Properties of the fluid to be measured such that : pressure transmitter air, pressure transmitter gas,
Properties of the fluid to be measured such that : pressure transmitter air, pressure transmitter gas, 
 Functional safety and safety integrity level (SIL) ;
Functional safety and safety integrity level (SIL) ;  The gauge pressure
The gauge pressure The pressure transmitter differential or pressure transmitter deltaP
The pressure transmitter differential or pressure transmitter deltaP The pressure transmitter absolute
The pressure transmitter absolute
 The pressure transmitter diaphragm
The pressure transmitter diaphragm

 Visit industrial pressure transmitters require periodic calibration to ensure
Visit industrial pressure transmitters require periodic calibration to ensure 

 A pressure transmitter 4-20 mA can be tested by applying a defined known pressure to the mechanical interface of the pressure sensor and checking the measured analog output signal. If you have a pressure transmitter with displaycheck the value displayed on the indicator.
A pressure transmitter 4-20 mA can be tested by applying a defined known pressure to the mechanical interface of the pressure sensor and checking the measured analog output signal. If you have a pressure transmitter with displaycheck the value displayed on the indicator.

 Understanding
Understanding 

 Visit pressure measurement requires call in the professionals in the instrumentation sector.
Visit pressure measurement requires call in the professionals in the instrumentation sector.











